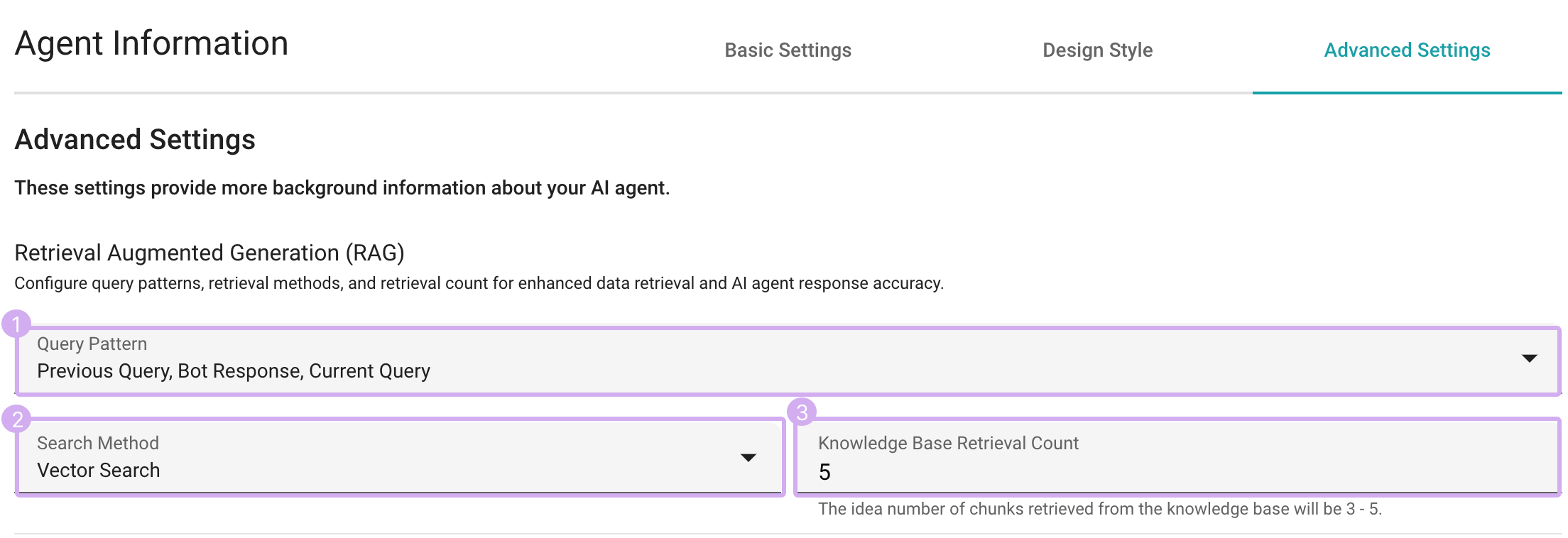
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
Overview
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a pivotal feature within SeaChat, enhancing data retrieval and augmenting the accuracy of interactions with the AI agent. It provides you with the ability to change settings for Query Pattern, Search Method, and Knowledge Base Retrieval Count. By experimenting with these settings, you can customize how your AI agent interacts with the knowledge base efficiently.
Query Pattern
Whether you require comprehensive context, focused engagement, or quick, precise responses, SeaChat’s flexible query patterns for querying the knowledge base ensure an optimized chat experience tailored to your preferences.
The following is an example conversation between a customer and a parking lot FAQ AI agent with information of more than hundreds of parking lots in the knowledge base:
👨 (Previous Query): Is there a parking lot near the Seattle Space Needle?
🤖️ (Bot Response): Yes, you can park at the ABC Parking Lot on 123rd Ave NE. It has 50 parking spots. The parking fee starts at $10 per hour, with a daily maximum of $60.
👨 (Current Query): I will be working near there. Can I rent a parking spot monthly?
Previous Query → Bot Response → Current Query
Offers comprehensive context by incorporating the last three turns of the conversation. In this case, the complete conversation (Previous Query + Bot Response + Current Query) is used to query the knowledge base and to generate the AI agent’s next response for Current Query.
Previous Query → Current Query
Focuses more heavily on the user’s requests and is not influenced by the AI agent’s response. It includes the last two user inputs (Previous User Query and Current User Query) to query the knowledge base and to generate the AI agent’s next response.
Current Query
Provides a succinct approach, considering only the user’s latest input, i.e. Current User Query, for the AI agent’s next response. This is ideal for one-turn dialogues or cases where users frequently switch topics. However, it may miss important context when discussing the same topic over multiple turns.
Search Method
You can optimize knowledge base search by choosing from distinct knowledge base search methods:
Keyword Search
Matches user’s provided keywords against the knowledge base to deliver relevant results. This works well when you have unique tokens such as product names, locations, IDs, etc. but may miss cases where the user doesn’t say the exact keyword (for example, they use a synonym or a different language than the KB document).
Vector Search
Utilizes the capabilities of text embedding to enhance the retrieval of relevant information. Vector search can work well across languages and retrieve similar documents even if they don’t have matching keywords. However, it may struggle with rare tokens such as product names, locations, or IDs.
Hybrid Search
Integrates both Keyword and Vector Search methods to optimize information retrieval.
Knowledge Base Retrieval Count
Changing Knowledge Base Retrieval Count allows you to specify the number of KB documents(chunks) to retrieve, ensuring efficient information retrieval. These retrieved documents will serve as important contexts for AI agent responses at each turn. The ideal count is flexible and depends on the token limits and document types.
Considerations for setting the count
- Too Few Documents/Chunks
You may miss essential information, leading to incomplete or inaccurate responses from GPT.
- Too Many Documents/Chunks
Important information may get buried under irrelevant details, making it harder for GPT to provide accurate responses.
- Context Limit
There is a limit to the amount of context that can be provided with each request. If the retrieved documents exceed this limit, SeaChat will use as many documents as can fit within the limit.
By adjusting the KB retrieval count, you can optimize the balance between depth of information and resource usage, ensuring accurate and efficient responses.